고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
Kaggle 신용카드 사기 검출
https://www.kaggle.com/mlg-ulb/creditcardfraud
Credit Card Fraud Detection
Anonymized credit card transactions labeled as fraudulent or genuine
www.kaggle.com
Credit Card Fraud Detection
- creditcard.csv (284,807 * 31)
- Class : 0 (정상), 1 (사기)
- 사기 검출(Fraud Detection), 이상 탐지(Anomaly Detection)
1. Google Drive Mount
#'creditCardFraud.zip' 파일을 구글드라이브에 업로드 후 진행
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')!ls -l '/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/datasets/creditCardFraud.zip'2. Data Preprocessing
2-1. Unzip 'creditCardFraud.zip'
!unzip /content/drive/My\ Drive/Colab\ Notebooks/datasets/creditCardFraud.zip!ls -l
2-2. 데이터 읽어오기
import pandas as pd
DF = pd.read_csv('creditcard.csv')
DF.info()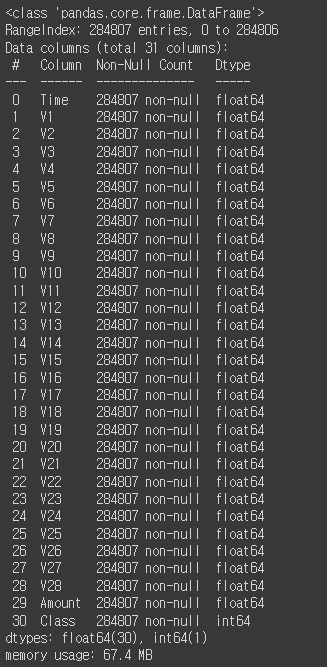
DF.head()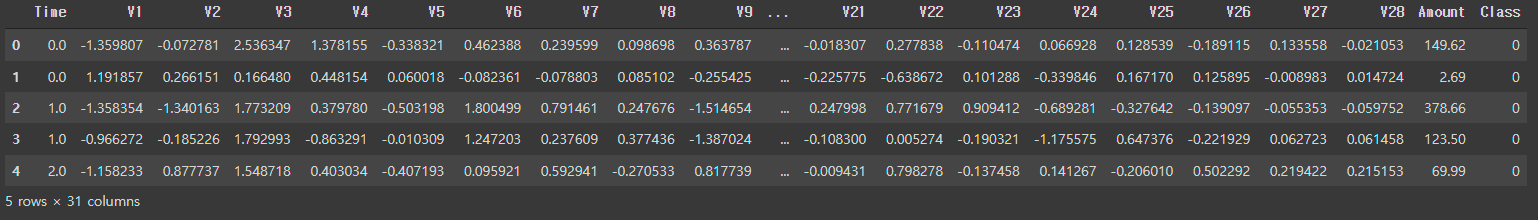
#0 (정상) Class와 1 (사기) Class 개수
DF.Class.value_counts()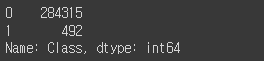
#0 (정상) Class와 1 (사기) Class 비율
(DF.Class.value_counts() / DF.shape[0]) * 100
2-3. Time 열(Column) 삭제
DF.drop('Time', axis = 1, inplace = True)
DF.head(1)
2-4. train_test_split( )
X = DF.iloc[:,:-1]
y = DF.iloc[:, -1]
X.shape, y.shape((284807, 29), (284807,))
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y,
test_size = 0.3,
random_state = 2045,
stratify = y)
X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_test.shape((199364, 29), (199364,), (85443, 29), (85443,))
#Train_Data와 Test_Data의 1 (부정) 비율이 균형
print('Train_Data :','\n', (y_train.value_counts() / y_train.shape[0]) * 100)
print('Test_Data :','\n', (y_test.value_counts() / y_test.shape[0]) * 100)
3. Keras Modeling
3-1. Model Define
import tensorflow
from tensorflow.keras import models
from tensorflow.keras import layers
ccfd = models.Sequential()
ccfd.add(layers.Dense(128, activation = 'relu', input_shape = (29,)))
ccfd.add(layers.Dense(64, activation = 'relu'))
ccfd.add(layers.Dense(32, activation = 'relu'))
ccfd.add(layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid'))#모델 구조 확인
ccfd.summary()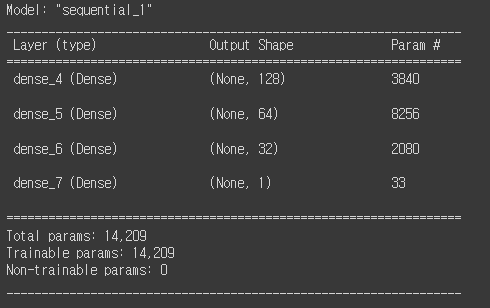
3-2. Model Compile
ccfd.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy',
optimizer = 'adam',
metrics = ['Recall'])3-3. Model Fit
%%time
Hist_ccfd = ccfd.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs = 50,
batch_size = 1024,
validation_data = (X_test, y_test))
3-4.학습 결과 시각화
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
epochs = range(1, len(Hist_ccfd.history['loss']) + 1)
plt.figure(figsize = (9, 6))
plt.plot(epochs, Hist_ccfd.history['loss'])
plt.plot(epochs, Hist_ccfd.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('Training & Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend(['Training Loss', 'Validation Loss'])
plt.grid()
plt.show()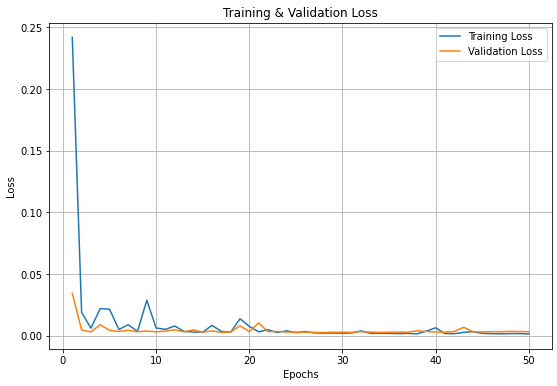
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
epochs = range(1, len(Hist_ccfd.history['recall']) + 1)
plt.figure(figsize = (9, 6))
plt.plot(epochs, Hist_ccfd.history['recall'])
plt.plot(epochs, Hist_ccfd.history['val_recall'])
plt.title('Training & Validation Recall')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Recall')
plt.legend(['Training Recall', 'Validation Recall'])
plt.grid()
plt.show()
3-5. Model Evaluate
loss, recall = ccfd.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print('Loss = {:.5f}'.format(loss))
print('Recall = {:.5f}'.format(recall))
3-6. Model Predict
import numpy as np
y_hat = np.round(ccfd.predict(X_test))
y_hat
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix(y_test, y_hat)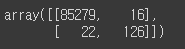
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
print(accuracy_score(y_test, y_hat))
print(precision_score(y_test, y_hat, pos_label = 1))
print(recall_score(y_test, y_hat, pos_label = 1))
728x90
'인공지능 > 실습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CIFAR 10 - Categorical Classification (0) | 2022.06.24 |
|---|---|
| Fashion MNIST - Categorical Classification (0) | 2022.06.20 |





